中文原文地址:http://www.eoeandroid.com/thread-258233-1-1.html
英文原文地址:http://developer.android.com/training/articles/perf-anr.html
It's possible to write code that wins every performance test in the world, but still feels sluggish, hang or freeze for significant periods, or take too long to process input. The worst thing that can happen to your app's responsiveness is an "Application Not Responding" (ANR) dialog.
编写的代码能够通过每一个性能测试,但在有些时候,仍然感觉程序有明显的停顿,或是需要很长时间才能处理输入。最糟糕的事情是在程序中弹出“应用没有响应”(ANR)对话框。
In Android, the system guards against applications that are insufficiently responsive for a period of time by displaying a dialog that says your app has stopped responding, such as the dialog in Figure 1. At this point, your app has been unresponsive for a considerable period of time so the system offers the user an option to quit the app. It's critical to design responsiveness into your application so the system never displays an ANR dialog to the user.
在Android中,系统为了防止应用程序在一段时间内反应不足,就会弹出一个对话框说明你的应用程序已经停止响应。当出现这个情况,说明你的应用程序已经在相当长的一段时间内没有响应,所以系统为用户提供了一个选项,来退出应用程序。所以关键是要设计好程序的响应机制,系统不会显示ANR对话框。
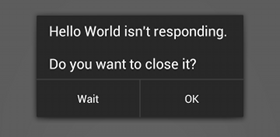
This document describes how the Android system determines whether an application is not responding and provides guidelines for ensuring that your application stays responsive.
什么引发了ANR?
Generally, the system displays an ANR if an application cannot respond to user input. For example, if an application blocks on some I/O operation (frequently a network access) on the UI thread so the system can't process incoming user input events. Or perhaps the app spends too much time building an elaborate in-memory structure or computing the next move in a game on the UI thread. It's always important to make sure these computations are efficient, but even the most efficient code still takes time to run.
一般来说,当应用程序不能响应用户输入时,系统就会显示一个ANR对话框。例如,应用程序由于在UI线程上的一些I/O操作而阻塞(访问网络),系统就不能处理用户输入。或者应用程序在UI线程中花费太多的时间来建立一个复杂的结果或者在游戏中计算下一步行动。非常重要的一点是确保这些计算式高效的,但即使最高效的代码仍然需要时间来运行。
In any situation in which your app performs a potentially lengthy operation, you should not perform the work on the UI thread, but instead create a worker thread and do most of the work there. This keeps the UI thread (which drives the user interface event loop) running and prevents the system from concluding that your code has frozen. Because such threading usually is accomplished at the class level, you can think of responsiveness as a class problem. (Compare this with basic code performance, which is a method-level concern.)
当程序需要执行很长时间的操作时,不应该在UI线程中执行,应该创建一个后台线程来处理任务。这使得UI线程能够正常运行,防止系统认为你的程序无响应。因为通常这些线程在类的级别中完成,你可以认为响应问题是一个类的的问题。
In Android, application responsiveness is monitored by the Activity Manager and Window Manager system services. Android will display the ANR dialog for a particular application when it detects one of the following conditions:
- No response to an input event (such as key press or screen touch events) within 5 seconds.
- A BroadcastReceiver hasn't finished executing within 10 seconds.
在Android中,应用程序的响应是由Activity Manager和Window Manager系统服务来监控的。当应用发生下面的情况时系统会显示ANR对话框:
- 在5秒内没有对用户的输入做出响应。
- 一个BroadcastReceiver在10秒内没有完成执行。
如何避免ANR
Android applications normally run entirely on a single thread by default the "UI thread" or "main thread"). This means anything your application is doing in the UI thread that takes a long time to complete can trigger the ANR dialog because your application is not giving itself a chance to handle the input event or intent broadcasts.
Android的程序默认都执行在一个UI线程或主线程。这意味着在UI线程中需要长时间完成的操作都能触发ANR弹窗。
Therefore, any method that runs in the UI thread should do as little work as possible on that thread. In particular, activities should do as little as possible to set up in key life-cycle methods such as onCreate() and onResume(). Potentially long running operations such as network or database operations, or computationally expensive calculations such as resizing bitmaps should be done in a worker thread (or in the case of databases operations, via an asynchronous request).
因此,在UI线程上面运行的任何方法都应该尽可能少的执行操作。尤其是在Activity的一些生命周期的函数中,例如onCreate(),onResume(),都应该尽可能少的执行操作。一些潜在的操作,例如网络和数据库操作,或一些费时计算操作都应该运行在其他的工作线程中。
The most effecive way to create a worker thread for longer operations is with the AsyncTask class. Simply extend AsyncTask and implement the doInBackground() method to perform the work. To post progress changes to the user, you can call publishProgress(), which invokes the onProgressUpdate() callback method. From your implementation of onProgressUpdate() (which runs on the UI thread), you can notify the user. For example:
对于耗时操作创建工作线程最有效的方式就是使用AsyncTask类。可以简单的继承AsyncTask类,并在doInBackground()函数中执行操作。为了将执行进程传递给用户,可以调用publishProgress()函数,它将调用onProgressUpdate()回调函数。在onProgressUpdate函数中,可以通知用户。
private class DownloadFilesTask extends AsyncTask<URL, Integer, Long> {
// Do the long-running work in here
protected Long doInBackground(URL... urls) {
int count = urls.length;
long totalSize = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
totalSize += Downloader.downloadFile(urls[i]);
publishProgress((int) ((i / (float) count) * 100));
// Escape early if cancel() is called
if (isCancelled()) break;
}
return totalSize;
}
// This is called each time you call publishProgress()
protected void onProgressUpdate(Integer... progress) {
setProgressPercent(progress[0]);
}
// This is called when doInBackground() is finished
protected void onPostExecute(Long result) {
showNotification("Downloaded " + result + " bytes");
}
}
To execute this worker thread, simply create an instance and call execute():
执行这个工作线程,简单创建一个实例并调用 execute():
new DownloadFilesTask().execute(url1, url2, url3);
Although it's more complicated than AsyncTask, you might want to instead create your own Thread or HandlerThread class. If you do, you should set the thread priority to "background" priority by calling Process.setThreadPriority() and passing THREADPRIORITYBACKGROUND. If you don't set the thread to a lower priority this way, then the thread could still slow down your app because it operates at the same priority as the UI thread by default.
If you implement Thread or HandlerThread, be sure that your UI thread does not block while waiting for the worker thread to complete—do not call Thread.wait() or Thread.sleep(). Instead of blocking while waiting for a worker thread to complete, your main thread should provide a Handler for the other threads to post back to upon completion. Designing your application in this way will allow your app's UI thread to remain responsive to input and thus avoid ANR dialogs caused by the 5 second input event timeout.
如果你想要自己创建Thread类,你需要设置线程的优先级,调用Process.setThreadPriority()函数,并将THREADPRIORITYBACKGROUND设为优先级参数。如果你不将线程的优先级设低,该线程仍然会降低应用程序的响应速度,因为在默认情况下它的优先级与UI线程相同。与此同时,保证UI线程不会因为等待工作线程而阻塞,即不应调用Thread.wait()或Thread.sleep()函数。
The specific constraint on BroadcastReceiver execution time emphasizes what broadcast receivers are meant to do: small, discrete amounts of work in the background such as saving a setting or registering a Notification. So as with other methods called in the UI thread, applications should avoid potentially long-running operations or calculations in a broadcast receiver. But instead of doing intensive tasks via worker threads, your application should start an IntentService if a potentially long running action needs to be taken in response to an intent broadcast.
对于BraodcastReceiver执行操作的时间限制强调,BroadcastReceiver是用来执行一些:小的,离散的工作,例如保存设置信息或是注册一个Notification。如果响应BroadcastReceiver的消息,需要一个长时间运行的操作,可以启动一个IntentService来执行。
Tip: You can use StrictMode to help find potentially long running operations such as network or database operations that you might accidentally be doing your main thread.
加强响应
Generally, 100 to 200ms is the threshold beyond which users will perceive slowness in an application. As such, here are some additional tips beyond what you should do to avoid ANR and make your application seem responsive to users:
一般来说,用户在应用程序中感觉到停顿的时间阈值是100~200ms。下面是一些附加的建议帮助你的应用程序更好的响应用户输入:
- If your application is doing work in the background in response to user input, show that progress is being made (such as with a ProgressBar in your UI).
- For games specifically, do calculations for moves in a worker thread.
- If your application has a time-consuming initial setup phase, consider showing a splash screen or rendering the main view as quickly as possible, indicate that loading is in progress and fill the information asynchronously. In either case, you should indicate somehow that progress is being made, lest the user perceive that the application is frozen.
Use performance tools such as Systrace and Traceview to determine bottlenecks in your app's responsiveness.
如果应用程序在后台执行操作来响应用户输入,显示一个进度条。
特别是对于游戏,在工作线程中进行计算。
如果应用程序有一个耗时的初始设置阶段,考虑显示一个启动画面或进度视图,表明加载进度。应该以某种方式表明应用程序正在加载,否则用户会觉得程序无响应了。
使用性能工具,如Systrace和Traceview ,以确定您的应用程序的响应能力的瓶颈。
